Wireless Reading and Localization of Additively Manufactured Galinstan-Based Sensor Using a Polarimetric Millimeter-Wave Radar Imaging Technique
Abstract
DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2023.3294549
IEEEXplore: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10189355
Device
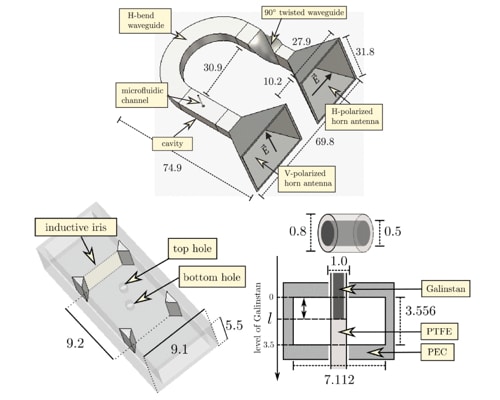
Polarimetric millimeter-wave radar used to read a passive temperature sensor with a microfluidic channel filled with Galinstan.
Spectrum
23.8 GHz for this particular demonstration of the reading technique
Novelty
Statistical estimation techniques using isolines computation and spatial averaging significantly reduces error contribution by waveguide variance (±20 µm), the meniscus of the Galinstan (±10 µm) and other contributors. Structural backscattering techniques that rely on the electromagnetic signature of the sensor, rather than sensing backscattering techniques that depend in part on the Galinstan level, successfully 3-D localizes the sensor and mitigates clutter in a vast majority of tested environments.
Performance
9.9 dB dynamic range, 4.5 dB/mm sensitivity at 2.4 m (0.9 dB at 14.8 m), ±10 µm or better accuracy after calibration for the environment