High-Frequency Doherty Versus Class-AB Power Amplifiers: What Is the Gain?
Abstract
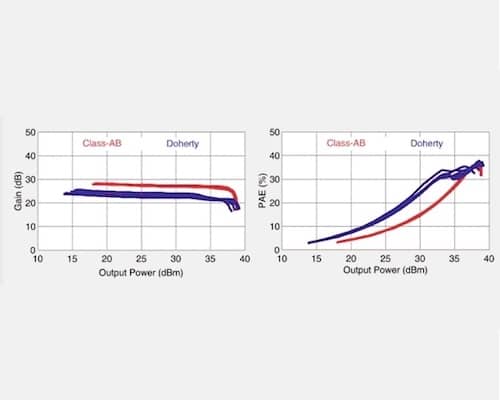
Doherty PAs may provide sufficient output power back-off efficiency (OBO) advantages to justify deployment versus class-AB PAs in applications that are not extremely cost-sensitive or robustness-demanding. Asymmetric device chains, additional biasing requirements and accurate modeling particularly for class C operation each contribute to Doherty PA cost and complexity compared to class AB PAs. Improved robustness under load variations can be achieved with isolated input and output combiners / splitters in the Doherty PA design that also contribute to cost and complexity. The choice of Doherty PAs does not necessarily incur a linearity penalty as shown in this article.
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11217213