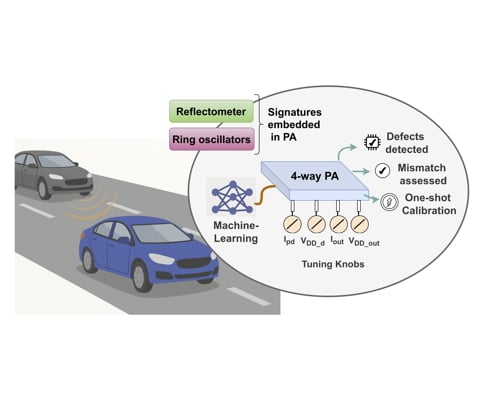
Machine Learning-Based Defect Detection, Output Matching Assessment, and Performance Recentering of a 79-GHz Four-Way CMOS Power Amplifier
Abstract
DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2025.3619021
IEEEXplore: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11215871
Device
Machine learning-based defect detection, output matching assessment, and performance recentering of a four-way CMOS power amplifier
Spectrum
79 GHz for this demonstration
Novelty
Defect detection is based on a defect filtering algorithm that employs outlier identification techniques. Mismatch evaluation employs a machine learning regressor. Performance calibration is based on a one-shot statistical calibration that predicts the optimum configuration of the PA
Application
To enhanced testability and performance calibration of power amplifiers (PAs) designed for 5G and beyond networks, automotive radar systems and the Internet-of-Things (IoT).
Performance
Power-added efficiency (PAE) RMS calibration error of 0.77% with predictive calibration model R2 of 0.71;
Drain efficiency (DE) RMS calibration error of 0.68% with predictive calibration model R2 of 0.78;
Power gain (Gp) RMS calibration error of 0.17 dB with predictive calibration model R2 of 0.93;
Saturated output power (Psat) RMS calibration error of 0.19 dBm with predictive calibration model R2 of 0.92.